Many protozoa live in the human body. Many of them are pathogens. Our story is one of them, the most. The opinion is based on both historical and recent publications.
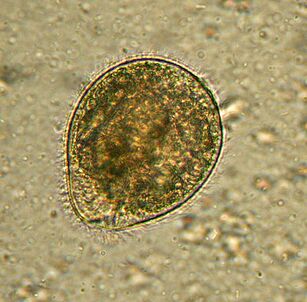
The largest. BalantidiumBalantidium coli
The largest protozoan is a human parasite and is the only silicate in the company. Sizes range from 30 to 150 microns and widths from 25 to 120 microns. For comparison: in the most advanced stage, the length of the malaria plasmodium is about 15 microns and several times shorter than that of the intestinal cells inhabited by ciliates. An elephant in a tile shop.
Wherever there are distributedpigs, they are the main carriers. It generally lives in the colonic submucosa, although it also occurs in the pulmonary epithelium in humans.B. colifeeds on bacteria, food particles, fragments of the host epithelium. In animals, the infection is asymptomatic. People may develop severe diarrhea with bloody, mucous discharge (balantidiasis), and sometimes ulcers on the walls of the colon. Death from balantidiosis is rare, but causes chronic exhaustion.
People become infected from contaminated water or food that contains cysts. The rate of infection in humans does not exceed 1%, and pigs can be infected all over the world.
Treated with antibioticsNo drug resistance has been reported for this cilia.
discoveredIn 1857 by the Swedish scientist Malstem. Today, balantidiasis is associated with tropical and subtropical areas, poverty and poor hygiene.
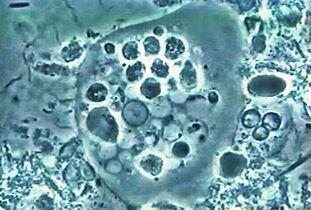
First. Oral amoebaEntamoeba gingivalis
The first parasitic amoeba in humans. A description of amoebae was published in 1849 in the oldest scientific journal. An amoeba was found on the dental plaque, hence the Latin gingivae - the name of the gum.
LivesAlmost all toothaches or gums hurt, live in gum pockets and plaques. Sometimes it feeds on epithelial cells, leukocytes, microbes and erythrocytes. It rarely occurs in people with a healthy mouth.
This small protozoan, measuring 10-35 cm, does not escape into the environment and does not form cysts; infecting another host with kissing, dirty dishes or contaminated food.E. gingivalisis considered an exclusive human parasite, but is sometimes found in captive cats, dogs, horses, and monkeys.
In the early twentieth century,E. gingivaliswas described as a causative agent of periodontal disease because it was always present in inflamed tooth cells. However, its pathogenicity has not been proven.
Drugs that affect this amoebaare unknown.
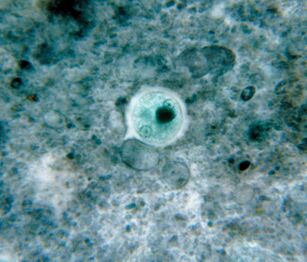
The most common. Amoeba dysenteryEntamoeba histolytica
This blood-borne intestinal parasite penetrates the tissues of the liver, lungs, kidneys, brain, heart, spleen and genitals. It eats food: food particles, bacteria, red blood cells, leukocytes and epithelial cells.
Widespread everywhere, especially in the tropics. Generally, people are infected by swallowing a cyst.
In mild countries, the amoeba usually remains in the intestinal lumen and the infection is asymptomatic. In the tropics and subtropics, the pathological process often begins:E. histolyticaattacks the walls. The reasons for the transition to the pathogenic form are not yet clear, but several molecular mechanisms of what has already been described. Thus, it is clear that amoebae secrete breakdown substances, pass through mucus and kill cells. As you can see, an amoeba can destroy a host cell in two ways: by triggering apoptosis inside it, or simply by chewing pieces. The first method has long been considered the only method. By the way, at a record speed - in a few minutes, the mechanism of cell suicide has not been determined. The second method was described very recently, the authors called it from the Greek "three" - trogocytosis for gnawing. It is noteworthy that the amoebae that bite the cell leave their prey as soon as they die. Others can completely phagocytose dead cells. Biting and eating cells are thought to differ in the gene expression model.
The penetration of amoebae into the bloodstream, liver and other organs is now associated with trochocytosis.
Amoebiasis is a deadly disease that kills about 100, 000 people each year from E. histolytica infection.
There is a non-pathogenic twin in the amoeba of dysentery,E. dispar, so a microscope is not enough to diagnose the disease.
To be treatedmust be destroyed mobileE. histolyticaand cysts.
DescribedE. histolyticaand in 1875 identified the pathogenic nature of a patient with diarrhea. The Latin name amoeba was given in 1903 by German zoologist Fritz Schaudin.Histolyticameans tissue destructive. In 1906, the scientist died of an amoebic intestinal abscess.
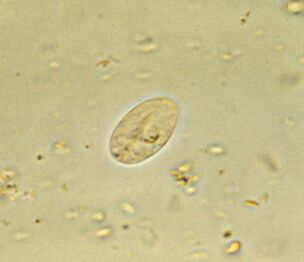
The most common. Intestinal lambliaGiardia lamblia (G. gastrointestinalis)
Giardia, the most common intestinal parasite, is ubiquitous. In developed countries, 3-7% of people are infected, and in developing countries 20-30%. That's about 300 million people.
Parasites live in the duodenum and bile ducts of the host they are swimming in, work with flags, and then attach to the epithelium with the help of a sticky disc at the bottom of the cell. For 1 cm2the epithelium adheres to one million lamblia. They damage the villi, which prevents the absorption of nutrients, causing mucosal inflammation and diarrhea. If the disease affects the bile ducts, it is accompanied by jaundice.
Giardiasis is a disease of dirty hands, water and food. The life cycle of a protozoa is simple: the intestine has an active form and stable cysts at the exit with fecal masses. In order to become infected, it is enough to swallow many cysts in the intestines, which will turn into an active form again.
The main secret of the ubiquity of lamblia in the variability of surface proteins. The human body fights antibodies against lamblia and, in principle, can develop immunity. However, people living in the same area and drinking the same water are repeatedly infected by the offspring of their parasites. Why? This is because during the transition from the active phase to the cyst and vice versa, the lamblia changes the proteins on which antibodies are produced - variant-specific surface proteins. There are about 190 variants of these proteins in the genome, but only one is present on the surface of an individual parasite; the translation of the rest is interrupted by an RNA interference mechanism. And change happens about once in about ten generations.
It is treated with an antiprotozoal substance with antibacterial activity. The disease passes within a week, but if it infects the bile ducts, relapse is possible for many years. Cysts fight water iodization.
Giardia lambliawas discovered in 1859 by the Czech scientist Wilém Lambl. Since then, several of the simplest names have changed, and the current name was given in honor of Alfred Giar, a French parasitologist who discovered and did not describe lamblia.
And Anthony van Leeuwenhoek made Giardia's first sketch, finding it in his sad chair. It was in 1681.
By the way, Giardia is also very old in terms of evolution, coming directly from the ancestor of almost all eukaryotes.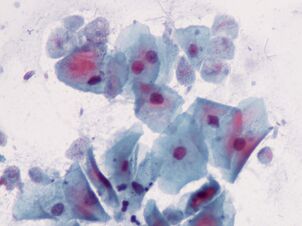
The closest. Trichomonas vaginalisTrichomonas vaginalis.
The simplest sexually transmitted. It lives in the vagina, in men - in the urethra, epididymis and prostate gland, is sexually transmitted or in wet clothes. Babies can be infected through the birth canal.T. vaginalishas 4 flagella and a relatively short wavy membrane at the anterior end; releases pseudopods when necessary. The maximum size of Trichomonas is 32 to 12 microns.
Trichomonas is more common than the causative agents of chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis. It affects about 10% and maybe more women and 1% of men. The latter figure is unreliable because it is more difficult to detect the parasite in men.
T. vaginalisThe microflora of the vagina, which maintains an acidic environment, feeds on microorganisms, including lactic acid bacteria, thereby creating an optimal pH of 4. 9 and above.
Trichomonas destroys mucosal cells and causes inflammation. About 15% of infected women complain of symptoms.
Treated with antibacterial drugs. To prevent this, it is recommended to wash regularly with diluted vinegar.
DescribedIn 1836 by the French bacteriologist Alfred Donne. The scientist did not realize that the pathogen was a parasite, but determined the size, appearance and type of movement of the simplest.
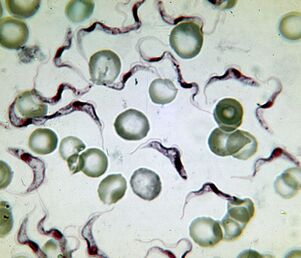
The most deadly. The causative agent of sleep disordersTrypanosoma brucei
The causative agent of African sleeping sickness is the most deadly protozoa. An infected person dies without treatment. Trypanosoma is a flagel that extends 15-40 um. There are two subtypes that do not differ in appearance. The disease causedT. brucei gambiense, lasts 2-4 years.T. brucei rhodesienseis a more virulent, transient pathogen that dies after a few months or weeks.
Distributed in Africa, between the 15th parallel of the Southern and Northern Hemispheres, in the natural range of the carrier - blood-sucking insects of the genus
From the gut of a flyT. bruceienters the human bloodstream, and from there into the cerebrospinal fluid and affects the nervous system. The disease begins with fever and inflammation of the lymph nodes, followed by lethargy, drowsiness, muscle paralysis, exhaustion and irreversible coma.
The lethality of the parasite is associated with its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Molecular mechanisms are not fully understood, but it is known that when entered the brain, the parasite secretes cysteine proteases and also uses some host proteins. On the other hand, trypanosomes in the central nervous system take refuge from immune factors.
The first description of sleeping sickness in the upper Niger was made by the Arab scholar Ibn Khaldun (1332-1406). In the early 19th century, Europeans were well aware of the first sign of the disease - swelling of the lymph nodes in the back of the neck (Winterbottom's symptom), and slave traders paid special attention to it.DiscoveredT. bruceiThe first Scottish microbiologist named David Bruce made the connection in 1903 between trypanosomes, tsetse fly and sleep disease.
Treatmentdepends on the stage of the disease, and medications cause serious side effects. The parasite has a high antigenic variability, so it is impossible to create a vaccine.
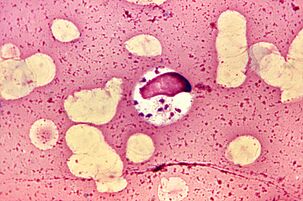
The most extravagant. LeishmaniaLeishmania donovani
Leishmaniasis is called the most extravagant parasite because it lives and multiplies in cells designed to kill parasites - macrophages.L. donovaniis the most dangerous of these. Visceral leishmaniasis, rheumatic fever, or cataracts, in which almost all patients die without treatment. However, survivors gain long-term immunity.
There are three subtypes of the parasite.L. donovani infantum(Mediterranean and Central Asia) mainly affects children, dogs are often its reservoir.L. donovani donovani(India and Bangladesh) is dangerous for adults and the elderly, there is no natural reservoir. AmericanL. donovani chagasi(Central and South America) can live in the blood of dogs.
L. donovaniis a flagpole no more than 6 microns long. Humans are infected withPhlebotomusmosquitoes, sometimes during sexual intercourse, babies - after passing through the birth canal. Once in the blood, the parasiteL. donovanipenetrates the macrophages that carry it through the internal organs. Reproductive parasites in macrophages destroy them. The mechanism of molecular survival in macrophages is very complex.
Symptoms of the disease- causes fever, enlarged liver and spleen, anemia and leukopenia, secondary bacterial infection. Every year, 500, 000 people are diagnosed with visceral leishmaniasis and about 40, 000 people die.
Treatmentsevere - intravenous administration and blood transfusion.
Taxonomic affiliationL. donovaniwas established in 1903 by Ronald Ross, a famous malaria researcher and Nobel laureate. The common name owes its name to William Leishman, and the special name to Charles Donovan, who independently discovered protozoan cells in the spleen of patients who died in 1903, one in London and the other in Madras.
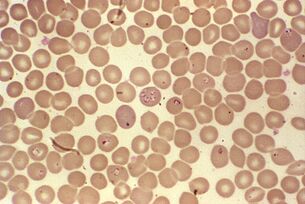
The most difficult period of life.Babesia spp.
Babesias,Ixodesgenus, along with multi-stage asexual reproduction in mammalian erythrocytes and genital mites in the intestines, complicates their development by transovarial transmission. From the intestines of the female tick, protozoan sporozoites penetrate the ovaries and infect the embryos. When the tick larvae emerge, the babesia passes into the salivary glands and enters the bloodstream of vertebrates with the first tooth.
spreadBabesia, America, Europe and Asia. Their natural reservoir is rodents, dogs and livestock. A person is infected with several types: B. microti, B. divergens, B. duncaniandB. venatorum.
The symptoms of babesiosis are similar to malaria - recurrent fever, hemolytic anemia, enlarged spleen and liver. Most people recover spontaneously, but babesiosis is fatal for patients with weakened immune systems.
Treatment methodsare still being developed, antibiotics are prescribed, and in severe cases, blood transfusions.
Babesia was described by Victor Babes (1888), a Romanian microbiologist who discovered sick cows and sheep.Haematococcus bovisdecided to deal with a pathogenic bacterium. Babesia was considered an animal pathogen for a long time until it was discovered in 1957 in a Yugoslav shepherd who died of B. divergens infection.
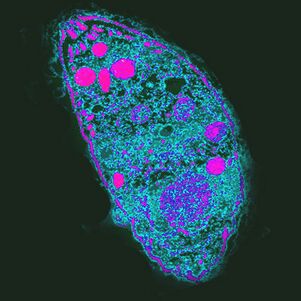
Most effective. The causative agent of toxoplasmosisToxoplasma gondii
T. gondiiis the most powerful parasite because it controls the behavior of intermediate hosts.
Distributed everywhere, unevenly distributed. For example, 84% of the population is infected in France and 22% in England.
The life cycle of toxoplasmosis consists of two stages: it occurs in any warm-blooded organism that is not sexual, sexual reproduction is possible only in the epithelial cells of the cat's intestine. ForT. gondiican complete development, the cat should eat an infected rodent. By increasing the likelihood of this occurrence,T. gondiiprevents the natural fear of rodents from the smell of cat urine and makes it attractive by targeting a group of neurons in the amygdala. It is unknown at this time what he did. One of the possible mechanisms of action is the local immune response to infection. Alters cytokine levels, which increase levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine. Toxoplasma also affects human behavior, which manifests itself at the population level. Thus, new situations are more common in countries with high levels of toxoplasmosis, neuroticism, and a desire to avoid uncertainty. Infection withT. gondiican cause cultural changes.
In humans,infectionis often asymptomatic, but with weak immunity, it destroys liver, lung, brain, and retinal cells, causing acute or chronic toxoplasmosis. The course of the infection depends on the virulence of the strain, the condition and age of the host's immune system - older people are less susceptibleT. gondii.
Treat toxoplasmosis with antiprotozoal drugs.
Describedin desert rodents in 1908. This honor belongs to Charles Nicolas and Luis Manso of the Pasteur Institute in Tunisia.
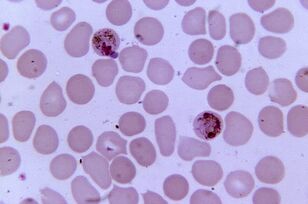
Most pathogenic. PlasmodiumPlasmodium spp.
Plasmodium malaria is the most pathogenic parasite in humans. The number of malaria cases can reach 300-500 million, and the death rate during epidemics can reach 2 million. The disease still kills three times more people than armed conflict.
Five types of Plasmodium cause malaria in humans:Plasmodium vivax, P. falciparum, P. malariae, P. ovaleandP. knowlesi, which also affect macaques.
DistributedIn the range of vectors - mosquitoesAnopheles, they should have a temperature of 16-34 ° C and a relative humidity of more than 60%.
Comparison of the genome ofP. falciparum, the most toxic substance in plasdia, with gorilla plasmodia shows that humans were infected by these monkeys by their ancestors. The emergence of this form of plasmodium is associated with the emergence of agriculture in Africa, which leads to an increase in population density and the development of irrigation systems.
Sexual reproduction of plasmodia occurs in the intestines of mosquitoes, and in the human body the intercellular parasite lives and multiplies in hepatocytes and erythrocytes until the cells explode. 1 ml of the patient's blood contains 1-50 thousand parasites.
The disease manifests itself as inflammation, periodic fever and anemia, and is dangerous for the mother and fetus during pregnancy.P. falciparumInfected erythrocytes clog capillaries and in severe cases develop ischemia of internal organs and tissues.
Treatmentrequires a combination of several drugs and depends on the specific pathogen. Plasmodia are resistant to drugs.






































